Components of nematode population assessment and community analysis
Sieving procedure: sieve angle.
Sieving procedure: sieve angle.
Sieving procedure: sieve angle.
Nematode extraction from soil
Sieving procedure: damaged equipment.
Careful and consistent technique.
Careful and consistent technique.
Careful and consistent technique.
Consider the biology of the organism.
Automating the procedure, reducing operator error.
Consistent procedure.
Automating the procedure, reducing operator error.
Automating the process: minimizing operator error.
Automating the process: minimizing operator error.
Automating the process: minimizing operator error.
Automating the process: minimizing operator error.
Soil cores must be disintegrated
Soil cores must be disintegrated
Soil cores must be disintegrated
Soil cores must be disintegrated
Cyst extraction: the Fenwick can.
Cyst extraction: the Fenwick can.
Mist chamber extraction.
Mist chamber extraction: water quality
Condition of the samples.
Condition of the samples.
Condition of the samples.
Condition of the samples.
Identification and counting.
Sampling and extraction.
Many procedures involve the use of sieves; careful and consistent procedure is essential.
Many procedures involve the use of sieves; careful and consistent procedure is essential.
Effective aperture size changes with sieve angle and blocking of sieve pores by soil particles.
Many procedures involve the use of sieves; careful and consistent procedure is essential.
Careful use of delicate equipment is essential. Sieves are easily damaged by fingernails and projecting objects.
Tissue paper extended over the edge of a Baermann funnel will act as a wick. Water will be wicked out of the funnel and contact between soil and water will not be maintained. Extraction of nematodes will halt.
Tissue paper extended over the edge of a Baermann funnel will act as a wick. Water will be wicked out of the funnel and contact between soil and water will not be maintained. Extraction of nematodes will halt.
Loss of contact between soil and water column.
Techniques such as the Baermann funnel require nematode movement. Ensure that temperature conditions are appropriate for nematode movement and consistent among samples that will be compared.
Oostenbrink elutriators; Wageningen, Netherlands, 1965.
A Baermann tray rack, Wageningen, Netherlands (Sharma, 1965).
Early version of the Byrd and Ferris elutriator; processing four samples on each cycle.
Use the valves and gauges to ensure equal water flow in multiple elutriator cones.
All components of the extraction process are conducted for the same time and intensity for each sample.
Ensure that all indicators are at the required setting for each sample.
Ensure that all indicators are at the required setting for each sample.
Intact cores may not break down during the extraction process; nematodes within the cores may not be extracted.
Intact cores may not break down in the elutriator.
Cores remain intact at the end of the elutriation cycle.
Cores remain intact at the end of the elutriation cycle; nematodes were not extracted from these cores.
Multiple Fenwick can extractors, Potato cyst nematode regulatory unit, Netherlands.
Separation of migratory endoparasitic nematodes from plant material.
What is the impact of water quality on separation of nematodes from plant material?
The extraction procedure only reveals information on the nematodes in the sample. Ensure that samples represent the nematode population in the field. Soil samples exposed to the sun are subjected to solarization effects: dead nematodes are not extracted by Baermann techniques.
Even the most skilled technician can only determine the number and types of nematodes in the submitted sample. Ensure that the sample represents the condition of the nematode community in the field.
|
|
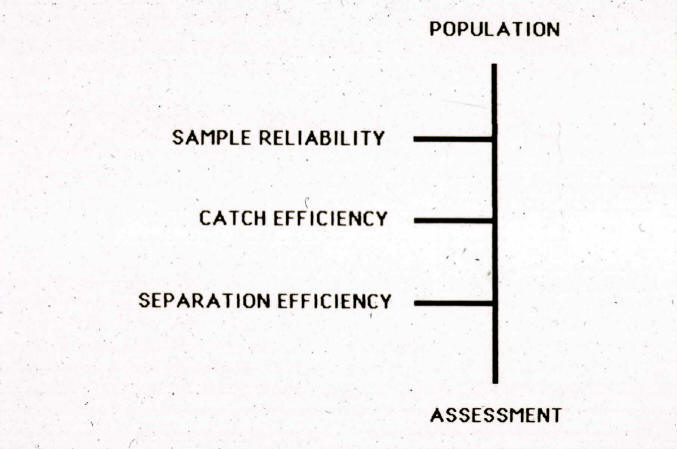
Components of nematode population assessment and community analysis
Sampling and extraction.