Family: Diplogasteroididae
Rev:
01/12/2026
- Chromadorea
Chromadoria
- Rhabditida
- Rhabditina
- Diplogastroidea
Diplogasteroididae
Filipjev & Schuurmans-Stekhoven, 1941
A note on the name of the order,
suborder, superfamily, family and subfamily:
Schultz (in Carus, 1857) erected and described the genus Diplogaster.
Through various taxonomic revisions and classification schemes, names at
different levels of resolution were derived from the genus name. Hence,
Diplogasterida, Diplogasterina, Diplogasteroidea, Diplogasteridae and
Diplogasterinae appear in the earlier (and some recent literature) as,
respectively, names for order, suborder, superfamily, family and subfamily.
Baker and Sanwal (1969) pointed out that the possesive case for the word ending
"gaster" would be "gastros", so that the latinized family name would have the
ending "gastridae", not "gasteridae" and likewise for the names of the other
taxonomic categories. Hence, in concordance with the International Code of
Zoological Nomenclature, the correct usage of the names is Diplogastrida,
Diplogastrina, Diplogastroidea, Diplogastridae and Diplogastrinae.
Interestingly, the family and subfamily names Diplogasteroididae and
Diplogasteroidinae, derived from the genus name Diplogasteroides are
unchanged, presumably because the possessive case is based on the word ending
"oid" rather than "er".
Modern Phylogenies:
The Order Diplogastrida is considered a suborder (Diplogastrina) of the
Rhabditida by Andrassy (2005) and as the superfamily Diplogastroidea within the
suborder Rhabditina of the order Rhabditida by DeLey and Blaxter (2002, 2004)
and
DeLey et al. (2006).
|
 |
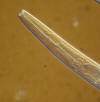 |
- Amphids pore-like, conspicuous at lwvel of upper region of stoma.
- Stoma tubular, length 3-6x greater than width, rhabditid like.
- Cheilostom wall not or slightly sclerotized
- Stegostom with very small denticles
- Anterior of esophagus with strong, mustcular metacorpus
- Posterior esophagus with small postcorpus
- Diselphic.
- Bursa very small
|
| |
|
|
References
Andassy, I. (2005) Free-living Nematodes of Hungary, Part I.
(Nematoda errantia). Hungarian Natural History Museum 518p.
Baker, A.D. and Sanwal, K.C. 1969. Some notes on nomenclature
(Nematoda). Journal of Helminthology 18:363-366.
Carus, J.V. 1857. Icones zootomicae. Rste Halfte: Die
wirbellosen Thiere 1pp.
De Ley, P. and Blaxter. M. 2002. Systematic position and
phylogeny. In: D. L. Lee (ed) The Biology of Nematodes.
De Ley, P. and Blaxter. M. 2004. A new system
for Nematoda: combining morphological characters with molecular trees, and
translating clades into ranks and taxa. Nematology Monographs and Perspectives, 2004:
633-653.
De Ley, P., Decraemer, W. & Eyualem-Abebe.
(2006). Introduction, summary of present knowledge and research addressing the
ecology and taxonomy of freshwater nematodes. Pp 3-30 in Eyualem-Abebe, Andrássy,
I. & Traunspurger, W. (Eds). Freshwater
Nematodes, Ecology and Taxonomy.
CABI Publishing,
Wallingford, UK.
Return to Diplogasteroididae Menu
Return to Order Menu
Go to Nemaplex Main Menu

