 Arthrobotrys
dactyloides, A. brochopaga. Arthrobotrys
dactyloides, A. brochopaga. |
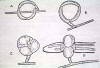 |
a) Constricting ring traps - what triggers traps? |
|
Rev 04/03/23
Trap formation is stimulated in presence of nematodes - older literature referred to "Nemin" as a specific and mysterious stimulant that emanated from nematodes. But trap formation probably can be stimulated by a variety of proteins and amino acids. Jaffee shows that traps can be stimulated by exposure to soil solution extract without nematodes.
Trapping mechanisms involve initial adhesion followed by lectin binding, followed by penetration peg and hyphal development. Is there attraction of the nematodes to the trap?
A large number of endozoic fungi trap nematodes. Some of these fungi are saprophytic but can be facultatively parasitic if resources are present. Others are obligate parasites but can be cultured on artificial media.
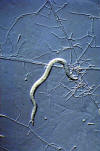
b) Sticky nets
|
 |
|
An example is Harposporium anguillulae, which has sickle-shaped spores that are ingested by bacterial feeding nematodes.
These fungi have motile zoospores that swim through natural body openings; zoosporangia fill body cavity. Could they be manipulated with irrigation? Catenaria spp.
| Pochonia chlamydosporia (formerly Verticillium chlamydosporium). Brian Kerry did extensive studies with this fungus as a regulator of Heterodera avenae in England. When cereals were grown, there was extensive damage due to the nematode initially, however after 7 years there was sufficient regulation of the nematode by the fungus to allow acceptable crop yields. |
Paecilomyces lilacinous, Dactylella oviparasitica are also egg parasites.
Australasian Plant Pathology Society Factsheets on Plant-parasitic Nematodes (Prepared by Dr. Graham R. Stirling)
(Use your Return Key or click the Index Tab to return to this Nemaplex page)