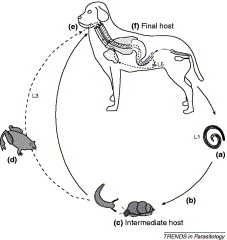
 |
Proposed life cycle of Angiostrongylus
vasorum, canine heartworm,
as an example:
(a) First-stage
larvae (L1) are passed out in the faeces of the final host. The
prepatent period is around 40-60 days, and larvae are reputedly egested
for many years after infection, and possibly for the lifetime of the
final host.
(b) L1
larvae infect molluscan intermediate hosts either by ingestion while
foraging on faeces or by penetration through the epidermis.
(c) Intermediate
host: several species of slug and snail have been infected
experimentally but it is not really known which species are most
important in nature. Larvae develop in the intermediate host, moulting
twice to reach the third stage (L3) after about 16 days.
(d) The
common frog (Rana
temporaria)
can act as a paratenic host after ingestion of infected slugs or snails,
and as an intermediate host after experimental infection with L1.
(e) L3
are ingested by the final host, either with an infected gastropod,
possibly food contaminated with snail or slug secretion (slime)
containing L3 larvae, or a paratenic host.
(f) Final
host: the fox and dog (and possibly also other wild canids and
mustelids) are final hosts. After ingestion, L3 penetrate the gut and
migrate to abdominal lymph nodes, where the third and fourth moults take
place.
The early L5 then enter the portal circulation and migrate through the
liver to reach the right ventricle and pulmonary arteries, where they
develop to the adult stage.
The female is oviparous and eggs are carried in the bloodstream to the
pulmonary capillaries. The eggs hatch and L1 penetrate into the alveoli,
migrate to the pharynx and are swallowed, to pass out in the faeces 1, 6. |