Molineus Cameron, 1923
Type species of the genus:
Molineus felineus Cameron, 1923
Synonyms:
Major characteristics of the genus:
- Synlophe bilaterally symmetrical with the cuticular ridges orientated
perpendicularly to the body surface;
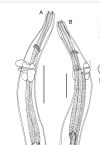
- In Molineus expectatus, esophagus surroundedby
irregullarly-shaped cuticular expansions just below circular excretory
furrow (Figs. A and B).
- Caudal bursa with a pattern of type 2-1-2 and 4 very short ray; the
extremities of rays 4 at mid-distance between those of rays 3 and 5;
- Female with a very short infundibulum.
|
|
Female:
- Didelphic
- Infundibulum a very short funnel-shaped structures between
ovaries and uterine branches.
Ref: Durette-Desset et al., 2020
|
Molineus inexpectatus:
A. female anterior, ventral view;
B:female anterior, right lateral view. Scale Bars A:100 um, B: 75 um
Drawings from Durette-Desset et al., 2000 |
|
Males:
- Bursa with a type 2-1-2 pattern and 4 very short ray; the
extremities of rays 4 at mid-distance between those of rays 3 and 5.
- Spicules nerrow
- Gubernaculum present.
|
Food Sources and Feeding strategies for the genus Molineus
Intestinal parasites of carnivorous mammals including Canidae and Felidae,
and neotropical primates. One species described from snakes.
Durette-Desset, M-C, Guerrero, R.A., Boyer, J. 2000. Two Trichostrongylina
(Nematoda) from Venezuela: a new species of Ornithostrongylus (Heligmosomoidea),
parasitic in birds (Columbiformes) and a new species of Molineus (Molineoidea),
parasitic in snakes (Squamata). Zoosystema 2000 22 (1)
Copyright © 1999 by Howard Ferris.
Revised:
October 16, 2025.