Rev. 01/20/2025
Phylum Nematoda
Class
Chromadorea
Subclass
Spiruria
Order Rhabditida
Suborder: Spirurina
Superfamily Habronematoidea
Habronematidae
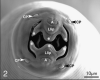
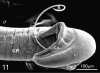
Nematodes of the family Habronematidae are intestinal parasites of birds and
mammals. The mammals are mostly equids (horses, ponies, donkeys, zebras)
where the skin, eye and intestine may be infected; the condition is known as
habronemosis.
The adult worms live under the mucous layer with their heads embedded in the mucosal spaces in the stomach. Commonly, first-stage larvae (from eggs produced by the adults) are found in host feces. Larvae of Habronema muscae develop to the infective stage in larvae and pupae of the housefly Musca domestica. Equines probably become infected by swallowing flies that fall into water or food. Larvae in ingested flies are liberated into the host stomach and grow to maturity within 2 months. The main effect of Habronema in the stomach is to stimulate hyperplasia and hypertrophy of the mucus-secreting cells and secretion of large amounts of thick, stringy, mucus. Effects on the host include gastritis, ulcers, diarrhea and weight loss have been reported in association with H. muscae infection (Naem, 2007).