Nematology 100 FINAL EXAM
December 11, 2012 2 hours
(45% of overall grade)
1.
(8 points)
a)
Describe the principles involved and discuss the mechanisms of nematode
management in the use of trap
crops.
b)
What types of nematode life history and feeding habits would be most susceptible
to this approach?
You are appointed as a member of a technical advisory committee to the
California Department of Food and Agriculture.
What actions (and why?) would you recommend if infestations of the burrowing
nematode, Radopholus similis, were
found in three newly-planted citrus orchards in southern California?
3.
(10 points)
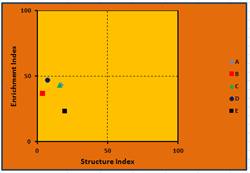
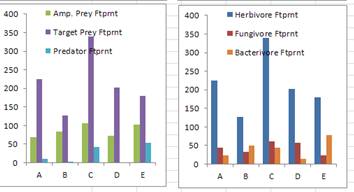
These three charts are based on
faunal analyses of five nematode samples from an abandoned field.


a)
Describe the apparent condition of the soil food web based on this faunal
analysis.
b)
What recommendations would you make for management of the soil food web if the
field was to be used for vegetable production in an organic farming system?
Indicate the intended purpose of each recommendation in relation to
services provided by various components of the food web
(use back of page).
4. (10 points)
True (T) or False (F)
a. Anguina agrostis is sometimes
associated with a bacterial infection of grasses caused by Clavibacter.
d. Species of spiral nematode,
Helicotylenchus,
behave as
migratory endoparasites
on some hosts.
5. (10 points)
Provide five differences in the life cycle, feeding habits, or host-parasite
relationships between the genera
Meloidogyne and
Heterodera.
Match the following. (Some letters may be used several times, others may not be
used at all. There may be several
answers to each question).
_______________1. Animal parasite
a)
Caenorhabditis elegans
_______________2. Damage to peanuts
b)
Pratylenchus vulnus
_______________3.
Predator
c)
Ditylenchus africanus
_______________4.
Microbivorous
d)
Rhabditis
spp
_______________5. Important on walnuts
e)
Xiphinema index
_______________6. Virus transmission
f)
Radopholus similis
_______________7. A-rated pest
(California)
g)
Trichinella spiralis
_______________8.
Migratory endoparasite
h)
Globodera pallida
_______________9. Suborder Tylenchina
i)
Ascaris suum
_______________10.Male does not feed
j)
Hemicycliophora arenaria
7. (18 points)
Based on your knowledge of nematode biology, available management tactics, host
ranges, etc., what control measures are available and practical for:
a) Root lesion nematode, Pratylenchus vulnus, in a nursery producing grape rootstocks.
b)
Anguina tritici
on wheat.
Describe the various ways that
elevated temperature
may be used to control plant-feeding nematodes. Include discussion on:
a) the advantages of each method.
b) the constraints of each method.
c) approaches that
enhance the efficacy of each
method.
d) the types of plants and nematodes for which such methods are most likely to
be useful.
9. (18 points)
a)
Heterodera glycines is an important economic pest of which crop in the
United States?
b)
Considering available strategies, including the most current information, design
a sustainable management plan for this nematode.
Explain the rationale for each component of your plan.