Chromadorea
Rhabditida
Tylenchina
Tylenchoidea
Pratylenchidae
Nacobbinae
Nacobbus bolivianus Lordello, Zamith and Boock,
1961
False Root-knot Nematode
Originally described as N. serendipiticus bolivianus by Lordello,
Zamith and Boock, 1961, the nematode was synonymized with N. aberrans
by Sher, 1970. Recent molecular and host-range studies show differences
among Central and South American populations of Nacobbus, with
populations from Bolivia and Peru disticnt from others. Consequently, Reid
et al. (2003). resurrected N. serendipiticus bolivianus and elevated it
to species status: N. bolivianus.
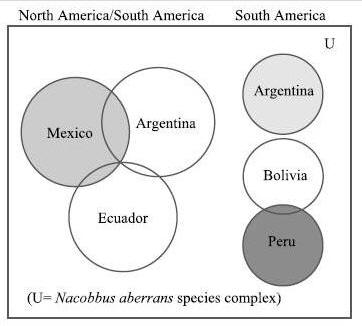 |
DNA sequences suggest three groupings of the Nacobbus
aberrans species complex: i) North/South American group of
populations from Mexico, Argentina and Ecuador; South American group
of by populations from Argentina; and Nacobbus bolivianus
represented by populations from Peru and Bolivia. Overlap of
circles represents shared DNA sequences.
Diagram from
Manzanilla-López et al. (2010). |
|
|
|
Bolivia and Peru.
Potato.
The nematode migrates through plant tissues as a juvenile; it initiates a
gall and becomes sedentary as a young female.
Manzanilla-López R.H. 2010. Speciation within Nacobbus:
consilience or controversy? Nematology 12:321-334.
Manzanilla-Lo
pez, R. H., M. A. Costilla, M. Doucet, J. Franco, R. N. Inserra,
P. S. Lehman, I. Cid del Prado-Vera, R. M. Souza, and K. Evans. 2002. The genus
Nacobbus
Thorne & Allen, 1944 (Nematoda:Pratylenchidae):Systematics,
distribution, biology and management. Nematropica 32:149-227.
Reid, A., Manzanilla-Lo
pez, R. H., Hunt, D.J. 2003. Nacobbus aberrans
(Thorne, 1935) Thorne & Allen, 1944 (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae); a nascent
species complex revealed by RFLP analysis and sequencing of the ITS-rDNA region.
Nematology 5:441-451.