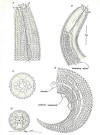
 . .
Encholaimus taurus
Golden & Murphy, 1967
A. Female anteriot, B, Immature molting. C; cross-section female. D.
Female en face, E. Male posterior.
Drawings from Golden and Murphy, 1967
|
-
Small nematodes. body 0.5-0.6 mm long
-
Cuticle tessellate with longitudinal and
transeverse striations
-
Amphid apertures oval
-
Six labial papillae, six 0uter labial setae
horn-like (cornuate), four smaller cephalic setae.
-
Odontostyle needle-like, odontophore with
flanges.
-
Esophagus terminating in pyriform bulb
-
Tails of both sexes conical
Female:
- Monodelphic, opisthodelphic
- Vulva a transverse slit
Male:
- Spicules dorylaimoid, paired; no gubernaculum
- Two preanal supplements
|