|
|
 |
|
One or two testes (monorchic/diorchic), one or two ovaries (monovarial/diovarial).
Single testis (monorchic) or two testes (diorchic),
spicules, gubernaculum, caudal alae are all of diagnostic value.
|
|
 |
|
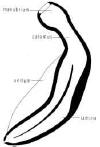
| Spicules - paired,
may be fused at tip.
Generally crescent-shaped, with distinct regions, and a cytoplasm core supplied with nerves. Their function is to spread vulva to allow entry of sperm. (Modified from Maggenti, 1981)
|
 |
 |
Size and shape of spicules
varies greatly among taxa.
The spicules provide useful diagnostic characters. (Modified from Maggenti, 1981) |
| Gubernaculum
If present is a guiding structure for spicules. Varies in shape. Often grooved. (Modified from Maggenti, 1981) |
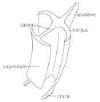 |
| The spicules may merely ride against the gubernaculum when
extended from the cloaca, or may slide along a track formed by the gubernaculum.
(Modified from Maggenti, 1981) |
|
| Supplements - glands of secretion and attachment. Ventromedian supplements have copulatory function. |

Male, Order Dorylaimida. Photomicrograph by I.A. Zasada |
| Rays - genital papillae embedded in caudal alae in some forms (sensory, tactile function?). | |
| Caudal alae (bursa) - cuticular in nature, see description under Cuticle. | |
| Sperm - generally non-flagellate, amoeboid. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Two other configurations of the female
reproductive system occur:
Additionally, ovaries may be variously reflexed and enlarged |
|
Return to Phylum Nematoda Menu